Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment For Achilles Tendon Pain
Achilles tendinitis is a condition that affects the Achilles tendon.
Achilles tendinitis is a painful ailment that results from inflammation, irritation, or degeneration of the Achilles tendon, which runs down the back of the lower leg.
Is there a variety of Achilles tendinitis?
Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment for Achilles Tendon Pain
Insertional and non-insertional Achilles tendonitis are the two kinds of Achilles tendinitis.
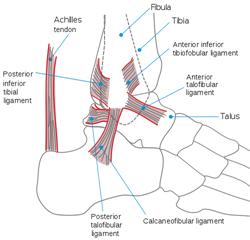
The lower section of the Achilles tendon, where it joins to the heel, is affected by insertional Achilles tendonitis. This type of Achilles tendonitis is characterized by small tears and swelling, and it is common in patients who have a Haglund’s deformity, a foot disease in which the back of the heel is prominent, causing tendon discomfort.
The middle section of the Achilles tendon is characterized by pain and inflammation in non-insertional Achilles tendonitis. Due to the stress and pull on the tendon, it can cause tissue degeneration. Young, energetic people are more likely to develop non-insertional Achilles tendinitis.
What causes Achilles tendonitis in the first place?
Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment for Achilles Tendon Pain
Repetitive stress and overuse are the most common causes of Achilles tendinitis. It can also be caused by a too rapid increase in physical activity. Other factors to consider include a pre-existing foot condition, aberrant bone growth, incorrect footwear, tight muscles or tendons, and even foot biomechanics like overpronation.
What are the signs and symptoms? What’s the best way to tell if you have it?
The following is a list of the most prevalent Achilles tendinitis symptoms:
Pain and stiffness along the Achilles tendon or the back of the heel, which is usually worse first thing in the morning.
Swelling and pain along the tendon or in the heel that gets worse with exercise
Swelling or thickening of the tendon
At the back of the heel, there is a bony protrusion or bone spur (insertional tendinitis)
Exercising causes severe discomfort the next day.
How can you know if you have Achilles tendinitis?
To check for calcification or bone formation in the tendon, doctors usually order an x-ray. The x-ray can reveal which portion of the Achilles tendon has become calcified. In insertional Achilles tendinitis, the lower section of the tendon becomes calcified. Non-insertional Achilles tendonitis is diagnosed when the central region of the Achilles tendon becomes calcified.
Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment for Achilles Tendon Pain
An MRI may be ordered by the doctor in some instances. When a clinician is concerned about major tendon tears, MRIs are employed. MRIs can reveal the extent of tendon injury and aid the doctor in planning surgery, as the type of surgery will be determined by the severity of the damage.
What can you do to avoid Achilles Tendinitis?
How to prevent Achilles tendonitis is one of the most frequently asked questions concerning the condition. Here are a few things you may do to reduce your chances of acquiring this ailment.
Exercising and overtraining should be avoided. Instead, progressively increase the intensity and duration of your workouts.
For long lengths of time, avoid running on soft terrain like sand or grass. Softer surfaces lead the heel of the foot to drop further than it would on a hard surface, putting more strain on the tendon.
Make sure you warm up properly before you exercise, and that you stretch not only before and after you exercise, but also on your rest days.
Make sure you’re wearing appropriate footwear. Wearing old, worn-out shoes that don’t give appropriate support is not a good idea. The Achilles tendon might be overworked if there isn’t enough support.
If you overpronate, you should wear a particular style of shoe that helps correct overpronation and has the following features: a. a solid heel counter that helps reduce overpronation. b. excellent arch support orthotic insoles c. Softer shoes at the rear of the heel can help to decrease tendon friction and irritation.
Shoes with ergonomic soles that provide a heel lift can aid to relieve tendon strain.
Orthotic insoles with anatomical arch support and heel lift are widely used to treat Achilles Tendinitis in shoes that lack suitable orthopedic qualities.
IDEASTEP offers a wide range of shoes and orthotics that can help with overpronation and Achilles tendon strain.
Learn more about how IDEASTEP shoes can help with Achilles tendon issues by clicking here.
What therapy alternatives are available?
Treatment options include both nonsurgical and surgical procedures. Surgical treatment is obviously a last resort, and it should only be considered if nonsurgical treatments have failed for at least six months.
Let’s start with the nonsurgical options:
Rest. Rest is at the top of the list of therapy alternatives. This entails either ceasing or at the very least reducing the activities that aggravate the discomfort.
Ice. Another alternative is to apply ice to the aching Achilles tendon area. This can be done at any time during the day and in up to 20-minute intervals.
Stretch your calf muscles. Calf stretches are beneficial because they strengthen the calf muscles while also reducing stress on the Achilles tendon.
Supportive footwear and orthotics are recommended. Softer shoes at the back of the heel can help to decrease tendon friction and irritation. Heel lifts in shoes can also aid to relieve strain on the tendon.
Learn more about how IDEASTEP shoes can help with Achilles tendon issues by clicking here.
Physical therapy is a type of treatment that involves the use of Physical therapy is one of the most effective ways to treat Achilles tendonitis. An eccentric strengthening program — a muscle tightening exercise for building strength and relieving stress – can be taught by a qualified physical therapist. It’s critical, though, that you have a professional physical therapist instruct you how to execute these exercises correctly, because doing them wrong might cause tendon injury.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These medications can help with pain and swelling throughout the rehabilitation phase, but they do not treat the tendon deterioration.
Now let’s look at surgical options:
The sort of surgery required is determined by the severity of the tendonitis and its location. Surgical procedures come in a variety of forms.
1. Tendon debridement and repair – this procedure is only conducted when the tendon is less than 50% damaged. The injured tendon is removed and the remaining tendon is restored using sutures in this procedure.
2. Debridement and tendon transfer – this procedure is utilized when the tendon has been damaged by more than 50%. An Achilles tendon transfer is a procedure that involves moving a tendon from the big toe to the heel bone.
3. Gastrocnemius recession – surgical calf muscle lengthening.
RELATED POST:




