Diabetic Orthotic Insole
Diabetic Foot (DF) refers to foot infections, ulcers, and/or deep tissue destruction caused by abnormalities in the distal nerves of the lower extremities and various degrees of peripheral vascular disease in diabetic patients. Clinically, it is mainly manifested as foot ulcers, which can involve various layers of tissues from the skin to the bones and joints. In severe cases, it may even require amputation. The occurrence and development of diabetic foot ulcers are the results of multiple factors, and elevated plantar pressure is an independent risk factor for foot ulcers. Increased plantar pressure as a predictor of foot ulcers has high sensitivity and specificity. A large number of clinical observations have confirmed that the correlation between the two is as high as 70% to 90%. Therefore, routine testing of the plantar pressure of diabetic patients has clinical significance for the prevention and treatment of diabetic feet. So how do you perform plantar pressure testing? Today, please follow us into the Department of Endocrinology (Chongqing Diabetes Center) of the First Hospital of Zhongyi Hospital to find out.
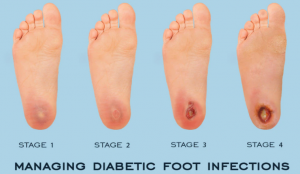
1. What is plantar pressure? Do all diabetic patients need to be tested?
Answer: Plantar Pressure refers to the overall vertical force between the sole of the unit area and the ground. Detecting the plantar pressure of diabetic patients can screen and find high-risk groups, diagnose diabetic foot early, determine the cause and severity of the foot disease, and provide a basis for early intervention and treatment. It is recommended that newly diagnosed diabetic patients and diabetic patients with a course of more than 5 years should undergo routine plantar pressure testing.
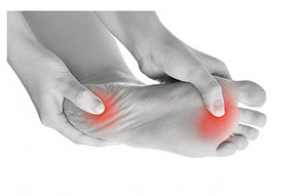
2. What are the causes of abnormal plantar pressure parameters and distribution in diabetic patients?
Answer: The parameters and distribution of plantar pressure of normal people have certain rules, and the abnormality or abnormal function of the feet in the disease state can lead to changes and abnormal distribution of plantar pressure. Among them, foot deformity is an important factor that causes excessive local pressure on the sole. Any deformity may cause the formation of high-pressure areas on the foot, leading to the formation of calluses, loose ligaments, joint disease, and then cause ischemia or abnormal gait and damage to the foot. The skin eventually forms ulcers. Studies have shown that the plantar pressure of diabetic patients is significantly higher than that of normal people, and the ratio of forefoot/hindfoot pressure in patients with peripheral neuropathy is increased.
3. What are the main foot deformities of diabetic patients?
Answer: There are flat feet, high arch feet, hallux valgus, and transverse arch collapse.
4. Can the existing technology quickly detect plantar pressure?
Answer: Our department now uses a foot pressure detector, the full name of which is an optical dynamic foot pressure detector. It can collect and analyze detailed plantar pressure data in a short period. It can measure the pressure distribution of the gradient, which can measure the pressure distribution with a minimum spacing of 2mm. The measurement range is: 350mm*150mm*2 (two-foot measurement), the measurement accuracy of the foot shape is ±1%. , And finally can form a dynamic foot pressure distribution video and report the static foot pressure distribution data of both feet.
5. What is the guiding significance of the application of the foot pressure monitor to the treatment of clinical patients?
Answer: The plantar pressure monitor uses pressure sensors and software to display plantar pressure maps, such as high-pressure areas (red) and bilateral pressure data, etc. After evaluation by professional medical personnel, the joint activities of lower limb joints, pelvis, spine, and other joints can be obtained. Whether the relationship is abnormal, and then provide effective decompression measures and diabetic foot prevention guidance for the patient’s situation.
6. What are the effective decompression measures for high-risk patients with diabetes with increased plantar pressure or uneven distribution?
Answer: Some surveys show that inappropriate footwear causes more than one-third of diabetic foot ulcers, and 85% of diabetic amputations are caused by foot ulcers. Therefore, it is a necessary and economical measure to achieve plantar pressure reduction by wearing suitable footwear. For patients with severe neuropathy, the ratio of the forefoot to hindfoot pressure is significantly higher. The increased pressure of the forefoot and imbalance of plantar pressure are important factors that are prone to ulcers on the forefoot. Such patients should wear special pressure relief shoes or use pressure relief diabetic orthotic insole.
7. How do ordinary diabetic patients choose suitable footwear?
Answer: You can refer when choosing shoes from the following aspects.
★ Length: When wearing shoes to stand and bear weight, you need to confirm that the shoes have sufficient length. The internal length of the shoes should be 1-2cm longer than the length of the foot measured from the heel to the longest toe.
★ Depth: It should be adapted to the free movement of the toes without causing pressure on the inside, outside, or back. ★ Width: The width should be equal to the width of all parts of the foot. If the upper is just right, the width is good. The relationship between the forefoot and the back foot is important because accommodating a wide forefoot may cause the heel to be too wide. ★ Height: The height may be lower than the ankle, flush with the ankle, or higher than the ankle. Premium shoes provide firmer, more stable, and reduced joint movement. High-top shoes also help decompress the forefoot.
★ Insole: The main function of the diabetic orthotic insole is pressure redistribution. This is achieved by the principle of increasing the contact area between the foot and the insole and adding corrective elements in the diabetic orthotic insole. Should use shock-absorbing, soft but flexible, and non-slip materials.
★ Outsole: Rubber, plastic, and leather can all be used to make shoe outsoles, but rubber outsoles are considered the best.
★ Heel enclosure: It is recommended to use a foot-fitting and closed heel, because footwear with an open back or too wide heel enclosure may cause heel injuries, and it is usually necessary for the wearer to hold the toes to keep the toes open state.
★ Heel lift: The heel height (or heel difference or spacing) should generally be 1.5-2 cm, and should not exceed 3 cm.
★ Closure: Properly tighten the shoelace or Velcro to keep the foot from sliding forward. The shoelace tightening should ensure long-term fastening and personal adjustment.
★ Uppers: uppers should be made of leather or synthetic materials (similar to sports shoes), smooth inner lining avoids materials that harden over time, limited seams, and best not in the upper area Seams and uppers should be breathable and durable and can improve foot deformities without creating pressure areas.
★ Toe box: The part of the shoe that covers and protects the toe should be soft (unless special requirements (such as construction professionals) require otherwise) and should be adapted to the shape of the toe to avoid any friction on the toe. (The above refer to Australia’s 2018 edition of “Guidelines for Wearing Shoes for Diabetic Patients”)
8. How do people at high risk of diabetic foot choose special pressure relief shoes?
Answer: People at high risk of diabetic feet should first pass the plantar pressure test to analyze the abnormal conditions of the individual plantar pressure, assess the risk of ulcers, and conduct private customization. The common ones are forefoot decompression therapy shoes, hindfoot decompression therapy shoes, honeycomb decompression insoles, diabetic orthotic insole, and so on. Patients can choose according to their situation.
Diabetic foot is a relatively common chronic disease of diabetes. It has a long treatment cycle, high cost, poor prognosis, and may even lead to amputation, which greatly impacts patients’ quality of life. Therefore, early prevention and early treatment are particularly important for patients. Plantar decompression is an important aspect of foot care for diabetic patients. Our department introduces advanced plantar pressure testing equipment and standardized diabetic foot treatment technology to protect your foot health!
