Overview
According to the shape and characteristics of the arch and the contact area with the ground, there are three types of feet: flat feet, normal feet, and high arch feet. High arch feet are about 12%, and the proportion of athletes is even higher to 20-25%. The so-called high arch foot is mainly manifested as the medial longitudinal arch is higher than the normal foot. The contact area of the sole and the ground is reduced, and the cushioning function of the foot is reduced.
Studies have shown that whether it is congenital or neurogenic high arch feet, the risk of foot injury (60%) is much higher than that of normal feet (23%). Williams et al. investigated the vulnerable parts of high arched runners and found that high arched feet have a higher probability of ankle joint, bone, and lateral injury. Powell et al. recorded the three-dimensional kinematics data of high arch feet and flat feet during barefoot walking and found that high arch feet have a smaller calcaneal valgus angle compared with flat feet. A comparative study of plantar pressure and gait characteristics between high arch feet and normal feet shows that compared with normal feet, high arch feet have less contact area, and the pressure on the heel and forefoot is higher than that of normal feet, thereby increasing the probability of hindfoot and forefoot foot injury is reduced, and the elastic function of the arch of the high arch foot is reduced, which leads to increased impact force of the knee joint meniscus and intervertebral disc, and increases the risk of soft tissue injury and pain in the knee joint, lower limb joint and spine joint.
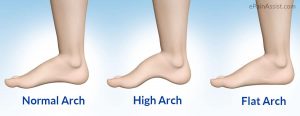
High arch foot
Two Clinical Manifestations and Biomechanical Characteristics of High Arch Foot
1. Clinical manifestations
High arch feet show that the medial longitudinal arch of the foot is too high, and the heel is inverted and stiff. Excessive traction of the plantar muscles, shortening of the Achilles tendon, slightly pointed posture, limited dorsiflexion, shortening and tightening of the plantar fascia, flattening of the transverse arch, and deformity of the claw-like toes. When standing with high arch feet, you can feel that most of the bodyweight is concentrated on the front and back of the feet. The arches on the inner soles of the feet are obviously abnormally high, the ligaments on the instep are too tight or the bones are deformed, resulting in the calcaneus and the toes.
The arch of the foot gradually becomes higher. At the same time, the high arch foot will cause the lateral angle of the knee joint to become larger, causing the lateral knee joint to open, causing knee joint disease, and making the downhill and stairs prone to fatigue and pain. Especially when the tension of the plantar tendons is uneven, symptoms such as pain in the transverse arch and plantar fascia cramps when walking, standing, and running are caused. High arch feet are also prone to shoulder and neck soreness, and even cause false long and short legs, scoliosis, plantar fasciitis, metatarsal inflammation, long calcaneal and metatarsal calluses, and easy inflammation of plantar ligaments complication.
In addition, the high arch feet have strong concealment, and they will not feel pain when they are young or in the early stage. They even feel that they are very agile. However, the weight of the feet of the high arch feet is unevenly distributed in the long term. In addition to the formation of the soles of the feet, the pain is caused by The walking style is prone to external rotation, the stability is not good, and other joints are more likely to cause excessive angle injuries.
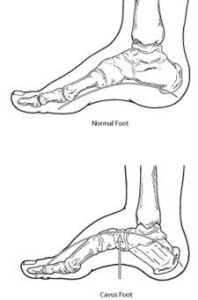
High arch foot
2. Biomechanical characteristics
In terms of ankle biomechanics, the high arch foot has the following main biomechanical characteristics:
a. From the perspective of bone structure
In the static state, the inclination angle of the heel bone of the hindfoot increases (generally greater than 60 degrees), the high position of the talus, the high position of the midfoot, and the increased plantarflexion angle of the forefoot.
b. From the point of view of the inner muscles and soft tissues of the plantar
Physical examination and ultrasound examination showed that the tension of the internal muscles, soft tissues, plantar muscles, and tendons of the foot increased.
c. From the perspective of plantar rolling gait analysis
During the four rolling processes of the sole, most of the high arch feet showed excessive inversion of the hindfoot and decreased cushioning function of the heel; insufficient pronation of the midfoot, reduced cushioning ability in the mid-term support, and shorter mid-stance time; rotation of the forefoot The front is insufficient and the adduction angle increases. In most cases, the first metatarsal head receives more force when it sinks and rolls, and when the fifth and fourth toes roll, the overall plantar rolling cushioning ability decreases.
High arch foot
d. From the perspective of plantar pressure and center of gravity shift
Increased force on the lateral side of the heel bone, increased force on the proximal and distal ends of the fifth metatarsal head, excessive pressure on the distal end of the first metatarsal head and thumb, and overall shifting of the center of gravity transfer line of the midfoot part.
e. Viewed from the movement of the ankle joint and lower limb joint chain
Intensified hindfoot varus, midfoot and forefoot excessive supination, forefoot slightly adduction, often compensatory causes knee, hip joint internal rotation, hyperextension, pelvic posterior lumbar lordosis, a series of generations such as reduced movement tendency Compensatory biomechanical abnormalities occur, leading to increased tension of the internal rotators of the corresponding lower extremities and stretching of the external rotators, further causing fatigue injury and pain of the external rotators of the knee and hip joints, and also the main cause of common pathological pain in the waist and trunk reason.
Hot blogs:
The Easiest Custom Insoles: Heat Moldable Insoles
Custom insoles, also known as orthotic insoles, are designed to provide personalized support and comfort for individuals with various foot conditions. In [...]
Children’s Insole Size Conversion Chart
The standard sizes for shoe insoles may vary from country to country, making it a headache to choose the right insole for [...]
Do custom orthotics need to be made by a doctor personally?
Custom orthotics do not necessarily need to be made by a doctor personally. While doctors, specifically podiatrists or orthopedic specialists, are often [...]
Do NBA players use custom insoles?
Custom insoles are not only helpful for people with foot health issues, but they also play a significant role in targeting the [...]
