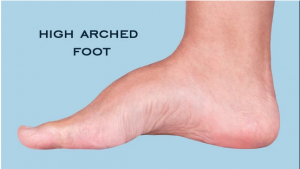
The high arch foot is a relatively common foot disease in children and adolescents, usual children with high incidence. Children are in an important stage of physical development, and the hazards of high arch feet need to arouse sufficient attention from parents. If you don’t get timely treatment, it will cause great distress to your child. The deformity of the high arch foot is easy to cause varus, valgus, and clubfoot. At this time, the child’s foot is likely to cause irreversible permanent damage due to the small area of force and high pressure.
High arch feet (also known as arch feet) are a common foot deformity, an abnormally elevated foot shape, mostly due to fixed plantar flexion of the forefoot caused by neuromuscular diseases, which increases the longitudinal arch of the foot. A small part of the disease is congenital, and most of it occurs after 3 years of age. It is caused by neurological disorders, such as tethered cord syndrome, syringomyelia, and hereditary neurological disorders. The common manifestations are shortened feet and raised midsections. When standing and bearing the weight, the stress points are mainly on the heels and the roots of the toes. At the same time, the toes may also have claw-shaped toes, sometimes combined with varus deformities.
The cause of the disease is very complicated. Most cases are neuromuscular diseases. The dynamic factors (such as tibialis anterior muscle or calf triceps muscle strength) that reduce the arch of the foot are weakened, and the internal muscles of the plantar side contracture, which causes the longitudinal arch of the foot. Increase. Some cases have a clear family history, but no evidence of neuromuscular disease, suspected of congenital disease, or idiopathic hyperarch, the specific classification is as follows:
①The gastrocnemius muscle is paralyzed, and its function is compensated by the plantar toe long flexor muscles at the beginning of walking, causing the interphalangeal joint to flex, and the forefoot droops, forming a high arched foot;
② Muscle fibrosis and contracture due to some reasons, and claw foot deformity can also be secondary;
③Some unexplained high arch feet often have a family history of the disease, and genetic factors are suspected to be involved in the disease, but genetic evidence is lacking;
④The tibialis anterior muscle is weak, and the peroneal muscle is strong. It pulls the first metatarsal bone and makes the foot pron. To compensate for the function of the tibialis anterior muscle, the contraction of each extensor muscle causes the metatarsophalangeal joint dorsal extension, thereby secondary toe flexor contraction Causes flexion of the interphalangeal joints.
High arch feet not only seriously affect the appearance, but also leave a huge hidden danger in terms of health. The typical high arched foot deformities are high arched, horseshoe, and claw-shaped toe deformities. The longitudinal arch of the foot is higher, the length of the foot becomes shorter, and the metatarsophalangeal joints are extended and the interphalangeal joints are plantarflexed. Achilles tendon contracture, plantar fascia contracture, tibialis anterior muscle weakness. The skin of the plantar metatarsal head may have corpus calluses and even necrosis. Most children with high arch feet cannot walk for a long time, and their feet are prone to fatigue and soreness. The feet are inelastic and the ankle dorsiflexion is limited. The high arch shape reduces the area of the plantar touching the ground, the soft tissue of the plantar weight-bearing area thickens, and the corpus callosum is formed and painful. However, for children with mild deformity, the deformity is reduced or even disappeared when standing weight-bearing, and the footprints are normal.
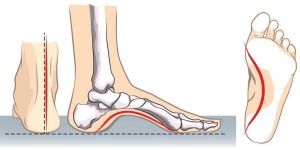
The help of orthotic insoles for high arch feet (1)
Our feet have to withstand the impact of thousands of walking or running and jumping every day. If not properly protected, it may cause damage to the feet and affect our daily life.
The medial arch is the first step in the human evolution of bipedal walking. It provides the toe flexor muscles with sufficient mechanical structure to support the body’s weight during the stance phase while helping to absorb shocks.
The collapse of the medial longitudinal arch is called “flat foot”; if the longitudinal arch is too high, it is called “high arch foot”. Since flat feet are easier to distinguish visually, there have been a lot of related studies in the past.
On the contrary, people with high arch feet, unless they are extremely deformed or combined with other major diseases, are not easy to see at a glance, so they have been ignored for a long time. People with high arches often feel pain in the back of their feet when wearing shoes, and it is difficult to find suitable shoes. The shoe wears out on the lateral side of the heel and the forefoot, and the calluses grow on the first and fifth metatarsal heads or the second toe bones of the hallux. If the hindfoot varus is prone to an ankle sprain, it is generally believed that the shock absorption ability of the high arch foot is poor, and it is difficult to stand for a long time or to walk for a long time, and it is easy to fatigue.
The help of orthotic insoles for high arch feet (2)
Orthotic insoles give the human body the force, which can redistribute the plantar pressure so that the human body can be in a correct state of biological force. The purpose of wearing orthotic insoles is to improve the body’s biological force line so that people can avoid the troubles and injuries caused by foot diseases. Because the clinical manifestations of high arch feet are not consistent, but the forefoot has fixed plantar flexion deformity. Toes are usually normal in the early stage. As the disease progresses, toes retreat, interphalangeal joint plantarflexion, metatarsophalangeal joint excessive back extension, and claw-like deformity. In severe cases, the toes cannot touch the ground.
![]()

Treatment of high arch foot orthotic insoles:
The foot has three main functions: cushioning, support, and rolling, so the high arch foot orthotic insoles must first meet the three major functional requirements. High arch feet often manifest as excessive flexion of the first metatarsal bone, excessive supination of the hindfoot, leading to the metatarsal passage and ankle sprain. Regarding this insole, we need to use orthotic insoles to give normal support to the arch of the foot, reduce the excessive pressure on the metatarsophalangeal joints, and at the same time increase the elasticity of the heel through special materials and improve the flexibility of the foot.
